They are currently recommended especially where they can not be placed compact low-power, as in bathrooms and hallways (CFL does not hold up well off and frequent or cold locations such as garages on):
- LED technology is low power consumption, with savings of 80-90% compared to incandescent and improving every year.
- Ecological; no Mercury or polluting materials, emits no UV or infrared.
- Lifetime: Duration between 20,000 and 50,000 hours, depending on the quality of the lamp and the LED.
- Instant light, as fast as incandescent or halogen.
- Can be switched on and off as many times as you want without reducing useful life.
- Because of its semiconductor format optimally support vibration and shock; it will work even if the casing is broken, contrary to the other technologies.
- With more lumens per cm2 than halogen and CFL, and more efficient, have great ability to be miniaturized (flashlights, televisions, etc).
- Uniform light without shadows into the light, available in warm white or pure, or all colors to consumer tastes.
- Design only limited by the imagination thanks to its compact size and low temperature of LED; the possibility of sharing the light sources as we want by the lamp allows innovative designs integrated into the environment ; are valid for any type of use.
- As in the CFL, some models can be adjusted easily by varying the electric current applied to a regulator. Very useful for environments that wish adaptive dynamic light environment (eg., We could program Arduino ambient lighting that adapts to the light coming through the windows, or human presence, illuminating more where people are ).
- The angle of the light from an LED is directed at an angle of limited brightness;There are lamps with angles between 30 and 240; laterally to illuminatemanufacturers seek designs where multiple LEDS pointing to different parts or modern reflectors, which can be a problem of space, and rising from the lamp, but gradually being solved with lenses that scatter light or formats led targeted less.
- Are still relatively expensive when it comes to high power systems where other lamps are almost as efficient and cheaper, such as sodium vapor (80 lm / W, but also more polluting and less durable), since the ledes require heat sinks (this will change as improve its luminous efficiency).
- The LED works better the white light is emitted (temp. Color approx. 6000K), for more warm yellow light to be mixed with another color decreases performance slightly.
- Require temperatures below 70 ° C to maintain their life, so they need efficient heat sinks, which increases their cost.
- They are very long lasting, but its intensity decreases with time; for an LED with an expected life of 25,000 hours, you will after that time a light intensity of 70% the original, but it will illuminate; not "merge" normally, but they fade away.
- The high power LEDs must wear a suitable light fader so that if viewed directly by accident, do not harm the view (some are more intense to look at the sun directly).
This entry will discuss technology LED and its many advantages, the influence of operating temperature on the duration (disarm a lamp) and uses more current recommended (for those who want to minimize investment while taking advantage of technology); go for the LED is a very good investment, ecological and profitable.
Save with LED technology
An LED is simply a semiconductor (bonding materials with special properties to conduct electricity), which converts the electrons into photons pass through the junction, ie light.
Depending on the semiconductor material, the light may be green, blue, infrared, ultraviolet, etc.
To protect the semiconductor contributing to heat dissipation have a layer of plastic (usually epoxy) which can act as a lens to focus light. More info: Wikipedia .
 |
| Source: Cree Corp. |
(Not to mention the inventor of the first practical LED, Oleg Vladimirovich Losev , who in 1927 developed the first LED and published the first study on this from their observations with the rectifier diodes used in radio, although his works were forgotten until 2007).
Now we can find lamps LED 850 lumens (comparable to a traditional 60W) for 20 €, and if we consider their performance (depending on the quality of the LED, but it is similar to fluorescent in most cases ) and its duration (maximum CFL lasts 8,000 hours, less the more you turn off and on), and comfort (is instantaneous), amortize a led light in about 2 years or less.
 |
| Source: LED Dossier |
The color temperature
Unless we change an incandescent or halogen light the other LEDs with the same color temperature, we can notice a big difference in color from light yellow if we almost pure white.
At first we can cost to get used to the difference in the color temperature of the lamp, but we can actually choose the warmth of the light from an LED, or Warm (3500ºK) or white light day (6000 ° K) (the pure sunlight has a temperature of 5770K), yet due to its light nature, normallyreproduces colors worse than sunlight.
There are LED lamps and LED lamps ...
The CRI (Color Rendering Index) value indicates the quality of color reproduction from the lamp; The closer to 100, the better.In the picture below, comparing with other traditional halogen LED warm white or cool.
 |
| Photo: Bartholomew Genovard |
Not all are equal. Normally, and as discussed below, should be done with lamps brand recognized for its quality as Philips. Chinese LED, but they are cheaper, will last less and less light per watt than brand because their lamps usually in the cheaper market semiconductor LED mounted.
Global manufacturers ledes include Nichia Corporation , Seoul Semiconductor , Create , Lumileds ,Epistar , Samsung and Osram .
The CREE and its clones are quite economical and efficient 80 to 100 lumens per watt in 2011.
To check worth while Chinese, I gained 6 cap format E27 € 10 per bulb and 420 lumens (similar to a 40W traditional ) by Ebay to check them and start using them in places where the light goes out / too frequently and CFL (compact fluorescent lamps) is not convenient to use, like the bathroom:
I could see its simplicity; SMD 5050 has 25 series, with an intermediate electronic transformer (wrapped in insulating plastic) that converts 220V AC to 70V DC, so each LED working at 2.8V (70/25 = 2.8).
Usually these lamps come with aluminum housing for better cooling, making them extremely expensive. However in this case the design could not be more economical, simple and effective;presents only vents just behind the LEDS plate appears sufficient to maintain a controlled temperature.
It reassembles every subject with tape and puts stress:
After half an hour the temperature stops rising, has almost reached 54 ° C, a very "healthy" for the semiconductor, and consistent with the characteristics announced temperature.
Sources:
LED Dossier; ETAP
Master's Thesis: Analysis of LED lighting for street lighting
Comparison of different types of lamp and lumens per watt efficiency.
The influence of temperature on the duration of the LEDs; Carandini
http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Led
http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sh%C5%ABji_Nakamura
Discussion on LED lamps Metalafición
Analysis (in French) about the dangers of LED
Global manufacturers ledes include Nichia Corporation , Seoul Semiconductor , Create , Lumileds ,Epistar , Samsung and Osram .
The CREE and its clones are quite economical and efficient 80 to 100 lumens per watt in 2011.
To check worth while Chinese, I gained 6 cap format E27 € 10 per bulb and 420 lumens (similar to a 40W traditional ) by Ebay to check them and start using them in places where the light goes out / too frequently and CFL (compact fluorescent lamps) is not convenient to use, like the bathroom:
NOTE: It is important to look at the lumens (amount of light) that gives the lamp, or we may fall short: If we replace a traditional bulb, we know as a traditional filament40W gives 495 lumens, a 60W -> 840 lm, one of 75W-> 1050 lm and a 100W-> 1400 lm.According to the seller, has the following technical characteristics:
- LEDES quantity: 25 SMD 5050
- Base type E27
- Consumption 6W
- Color range 4500 - 6000 K / Pure White
- Lumens 420 lumens (70 lm / W).
- Input voltage 220V.
- Duration 50,000 hours (Depending on the manufacturer)
- LED temperature <65 span="">
- Bulb temperature <60 span="">
- Dimensions Height: 78 mm. Diameter: 45 mm.
I could see its simplicity; SMD 5050 has 25 series, with an intermediate electronic transformer (wrapped in insulating plastic) that converts 220V AC to 70V DC, so each LED working at 2.8V (70/25 = 2.8).
The light emitted is very white, so the color is correct, and the lumens, compared to an incandescent 35W in the same bath, lights similarly:
If we do not get 420 lumens enough light, you can always buy these "thieves" for E27, very handy if you want to use lights, or in this case, expand and better distribute the light from these lamps:
The importance of temperature
The ledes last longer the lower is the junction temperature (in the semiconductor, where the light originates), so that an efficient system to remove the excess heat is very necessary.
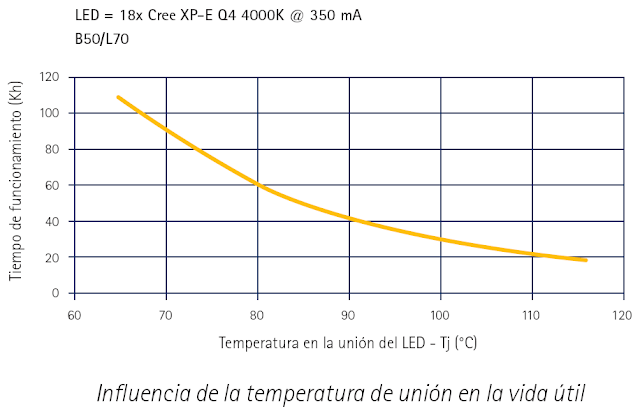 |
| Source: LED Dossier |
Usually these lamps come with aluminum housing for better cooling, making them extremely expensive. However in this case the design could not be more economical, simple and effective;presents only vents just behind the LEDS plate appears sufficient to maintain a controlled temperature.
The life of the LED's not only determines the junction temperature, but also the power that is required. The more electric current is applied, the more light, but also less durable. There are cheap LEDS that are overfed to illuminate more with less semiconductor material, thereby shorten its life at the expense of giving more light. In these cases, if we decide to or not rely on this data, it all depends on the manufacturer's reputation.
In addition, more current passes through an LED, it's lights, but lowering their performance as they apply more intensity (lumens / watt going down) to reach a plateau where all the extra electricity is converted into heat, stressing the LED (damaging it and shortening its life far). Manufacturers by tables indicate the optimum operating current and recommended; For example the novel MK-R CREE chip (4 leds power series inside) has a performance of 149 11,7V and 750mA lm / W, but if we lower the intensity at 350mA up 168 lm performance / W even reach 200 lm / W if you went down to 100 mA, but this intensity LED lights only, so it is not practical.
To verify that the temperature stays below 65 ° C as indicated by the manufacturer, with an ambient temperature of 22, I used the temperature sensor that I recently made with Arduino , hitting the sensor directly to the plate:
It reassembles every subject with tape and puts stress:
After half an hour the temperature stops rising, has almost reached 54 ° C, a very "healthy" for the semiconductor, and consistent with the characteristics announced temperature.
It remains only to check its duration, but time will tell. Currently we are using them for a month, and as the day;).
Where to use them
As with any investment, one should be cautious and make considering that it will continue to drop much in price, and install where it goes really profitable (alas if the government had been wiser and more farsighted if only a little. .. we would not be where we are ... :().
TIP: You should go slowly changing to LED lighting; as well as become cheaper quickly, its effectiveness is growing as technology improves (it's been giving 40 lm / W in 2004 to more than 70 lm / W in 2011, with a forecast of 170 lm / W 2015).
They are recommended for:
- Local high traffic but where the ignition timing is short (between 5 minutes and 1 hour), as rooms, bathrooms, hallways, kitchen extractor lights, etc.
- Inaccessible places, low maintenance LED will prevent us often change the lamp (p. Ex. High ceiling lamps in neighboring communities).
- Where its shock resistance and low power consumption are important, and flashlights.
If the lamp is going to be little used, it is best to use the incandescent reduced power while its price is not affordable.
The LEDs are ideal to place in conjunction with detectors, flashing not damaged.
And by this time I completed my analysis of the LEDs, increasingly present in our daily lives (screens, phones, etc) and now in our homes.
Given the rapid evolution of this technology, it is not surprising that in the coming years ledes are achieved with little loss of energy, or almost zero, and very cheap (less materials used).
By then we would have the perfect "bulb", and tungsten filaments form part of the story ...
Sources:
LED Dossier; ETAP
Master's Thesis: Analysis of LED lighting for street lighting
Comparison of different types of lamp and lumens per watt efficiency.
The influence of temperature on the duration of the LEDs; Carandini
http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Led
http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sh%C5%ABji_Nakamura
Discussion on LED lamps Metalafición
Analysis (in French) about the dangers of LED








No comments :
Post a Comment